What Is LiDAR? Definition, Technology, and How LiDAR Works in Drone Mapping?

Introduction
LiDAR has become a core technology behind high-accuracy drone mapping and surveying. From terrain modeling to infrastructure inspection, LiDAR enables drones to capture precise 3D data that traditional imaging methods often miss. According to NOAA, LiDAR is a remote sensing method that measures distances using laser pulses, creating highly accurate 3D representations of terrain and structures.
In this guide, we explain what LiDAR is, how LiDAR technology works, and why LiDAR drones are transforming mapping across industries.
Brief History of LiDAR Technology
According to Wikipedia “LiDAR technology originated in the 1960s, shortly after the invention of lasers. Early applications focused on atmospheric research and military use. Over time, advances in laser systems, GPS, and computing enabled LiDAR to become a key tool in mapping, surveying, and autonomous navigation.”
Today, LiDAR drones represent the most advanced and accessible form of this technology for commercial and industrial applications.
What Is LiDAR?
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) is a remote sensing technology that measures distances by emitting laser pulses and calculating the time it takes for those pulses to return after hitting an object. As explained by NEON, this process generates detailed 3D point clouds that map terrain, vegetation, and built structures with survey-grade precision.
Unlike standard cameras or GPS-based mapping, LiDAR delivers centimeter-level accuracy, works in low-light conditions, and can detect ground surfaces hidden beneath vegetation making it ideal for professional drone surveying and mapping.
What Does LiDAR Stand For?
LiDAR stands for Light Detection and Ranging.
It combines laser scanning with positioning systems to precisely measure distances and generate spatial data.
How Does LiDAR Work?
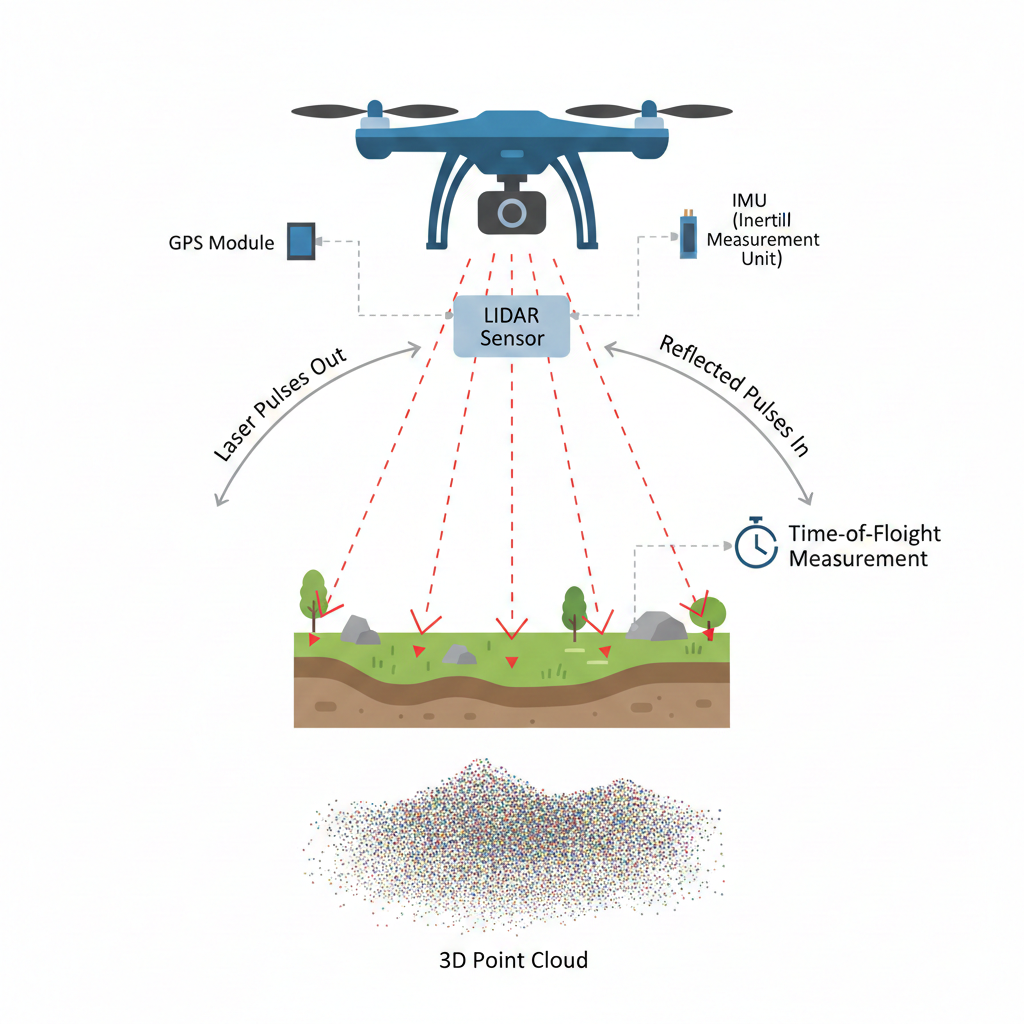
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) works by sending out rapid laser pulses toward the ground and measuring how long it takes for each pulse to return after hitting an object or surface. This method is based on a simple scientific principle called time of flight.
LiDAR Distance Calculation Principle
In simple terms:
Distance = (Speed of Light × Time Taken) ÷ 2
Because light travels extremely fast, LiDAR systems can calculate distance with very high accuracy, often down to a few centimeters.
Step-by-Step: How LiDAR Measures Distance
Laser Emission
The LiDAR sensor mounted on a drone emits thousands of laser pulses per second toward the ground or objects below.Reflection from Surface
These laser pulses hit surfaces such as buildings, trees, roads, or terrain and bounce back toward the sensor.Return Signal Detection
The LiDAR receiver captures the reflected light and records the time it took to return.Distance Calculation
Using the time delay and the speed of light, the system calculates the exact distance between the drone and the object.3D Point Cloud Creation
Each measured point is stored as a coordinate in 3D space. Millions of these points combine to form a highly detailed point cloud, which represents the shape and elevation of the scanned area.
How Accurate Is LiDAR?
LiDAR is known for its exceptional accuracy, often achieving centimeter-level precision when deployed correctly. Drone-based LiDAR systems typically deliver vertical accuracy ranging from 1–5 cm, depending on flight conditions and sensor quality.
Several factors influence LiDAR accuracy:
- Flight altitude and speed
- Sensor calibration and laser quality
- GPS and IMU precision
- Terrain complexity and vegetation density
Compared to traditional surveying methods, LiDAR drones provide highly reliable elevation data over large areas in significantly less time.
Factors That Affect LiDAR Accuracy
Several factors influence how precise LiDAR data is:
Flight altitude of the drone
Laser pulse frequency and power
GPS and IMU quality
Weather conditions (fog, heavy rain, dust)
Surface reflectivity (water and dark surfaces are harder to measure)
Higher-quality sensors and stable flight paths result in more accurate and consistent data.
Why LiDAR Can See Through Vegetation
Unlike cameras, LiDAR does not rely on visible images. Some laser pulses pass through gaps in leaves and branches and reach the ground.
This allows LiDAR to measure true ground elevation even in forests or dense vegetation, making it highly valuable for terrain mapping and environmental surveys.
Core Components of LiDAR Technology
LiDAR technology relies on several key components working in synchronization:
- Laser Scanner – Emits and receives laser pulses
- GPS Receiver – Records precise drone location
- IMU – Tracks orientation and motion
- Data Processing Software – Converts raw laser returns into usable 3D point clouds
Together, these elements allow LiDAR drones to deliver survey-grade spatial data.
Types of LiDAR Technology
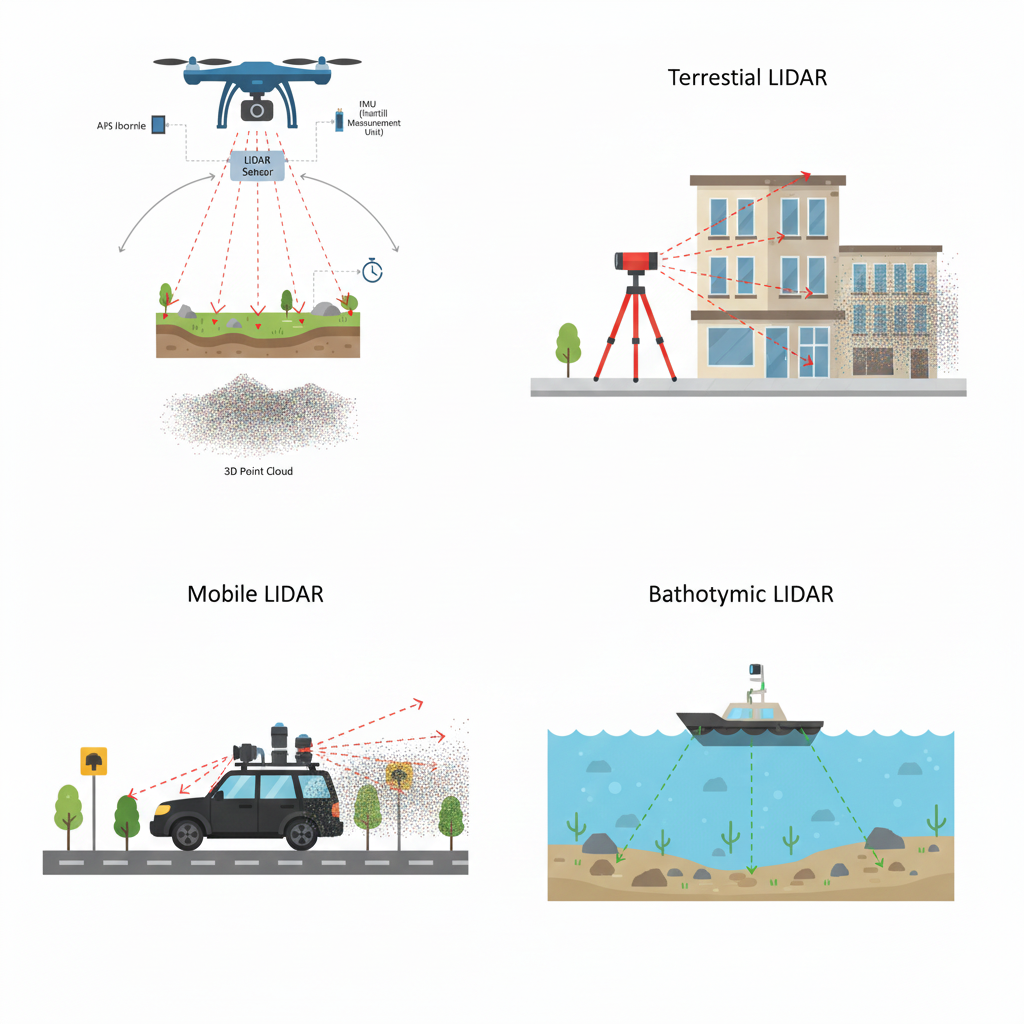
LiDAR technology is classified based on how and where it is deployed. Each type serves different mapping and sensing needs.
Airborne LiDAR
Mounted on drones or aircraft, airborne LiDAR is widely used for topographic mapping, land surveying, forestry analysis, and large-area data collection, taking full advantage of each platform’s payload capabilities.
Terrestrial LiDAR
Installed on ground-based tripods or vehicles, terrestrial LiDAR captures extremely detailed scans of buildings, infrastructure, and industrial sites.
Mobile LiDAR
Mounted on moving platforms such as vehicles or trains, mobile LiDAR is commonly used for road mapping, corridor surveys, and urban modeling.
Bathymetric LiDAR
Uses green laser wavelengths to penetrate water, enabling the mapping of riverbeds, coastlines, and shallow underwater terrain.
Benefits of LiDAR in Drone Mapping
- Exceptional Accuracy – Captures elevation and surface data with centimeter-level precision
- Fast and Efficient Surveys – Covers large areas significantly faster than ground-based methods
- Low-Light Performance – Operates effectively at dawn, dusk, or shaded environments
- Vegetation Penetration – Detects terrain beneath tree canopies
- Rich 3D Insights – Produces point clouds for volumetric analysis, topographic modeling, and 3D reconstruction
Common Applications of LiDAR Drone Technology
LiDAR drone mapping is widely used across industries, including:
- Topographic Mapping & Land Surveying – High-resolution elevation and contour maps
- Agriculture & Forestry – Tree height measurement, canopy density analysis, vegetation monitoring
- Construction & Mining – Site progress tracking, volume calculations, and compliance checks
- Infrastructure Inspection – Detailed geometry capture of bridges, pipelines, and power lines
- Environmental & Urban Planning – Flood modeling, erosion analysis, and city planning
These use cases demonstrate how LiDAR drones deliver speed, accuracy, and actionable data at scale.
LiDAR vs Photogrammetry
While photogrammetry uses images to calculate depth, LiDAR directly measures distance using laser pulses. This makes LiDAR more reliable in low-light conditions and in areas with limited visual features, such as forests or uniform surfaces.
Feature | Photogrammetry | LiDAR |
Data Source | Overlapping aerial images | Laser pulses measuring distance |
Lighting Dependence | Requires good lighting | Works in all lighting conditions |
Vegetation Penetration | Limited (canopy only) | High (ground beneath trees) |
Accuracy | Good, image-dependent | Very high (centimeter-level) |
Data Output | 2D/3D imagery | 3D point cloud |
Processing Time | Faster | Requires specialized processing |
Key takeaway: Photogrammetry is suitable for visual modeling and lower-cost projects, while LiDAR is the preferred choice for survey-grade accuracy and complex terrain mapping.
LiDAR vs Radar
Feature | LiDAR | Radar |
Wave Type | Laser light | Radio waves |
Range | Short to medium | Long-range |
Resolution | Very high detail | Lower resolution |
Weather Sensitivity | Affected by fog or heavy rain | Performs well in all weather |
Primary Use | Mapping and surveying | Detection and tracking |
Output | Detailed 3D point clouds | Object distance and movement |
Key takeaway: Radar excels in detection and long-range sensing, but LiDAR provides the fine detail required for precise mapping and modeling.
Limitations of LiDAR Technology
While LiDAR offers unmatched accuracy, it does have some limitations that should be considered:
- Weather Sensitivity – Heavy rain, fog, or dust can affect laser performance
- Higher Cost – LiDAR sensors and data processing are more expensive than standard imaging
- Complex Data Processing – Requires specialized software and expertise
- Limited Range – Effective over shorter distances compared to radar
Understanding these limitations helps businesses choose the right technology for each project.
Why LiDAR Is the Future of Drone Mapping?
LiDAR has become the gold standard for high-accuracy drone mapping, delivering precise 3D data that traditional imaging methods cannot consistently achieve. Its ability to penetrate vegetation, operate in low-light conditions, and produce survey-grade results makes LiDAR essential for industries that rely on accurate terrain and infrastructure data.
For industries using Drone as a Service (DaaS), LiDAR technology enables faster project delivery, reduced field costs, and data-driven decision-making across surveying, construction, forestry, and environmental monitoring. By combining advanced LiDAR sensors with professional drone operations, businesses gain reliable insights without investing in expensive hardware or in-house expertise.
As demand for precision mapping continues to grow, LiDAR-powered drone services are no longer optional, they are a competitive advantage.
FAQ Section
What does LiDAR stand for?
LiDAR stands for Light Detection and Ranging.
How does a LiDAR sensor work on drones?
It emits laser pulses and measures their return time to calculate precise distances and create 3D maps.
What’s the difference between LiDAR and radar?
LiDAR uses laser light for high-resolution mapping, while radar uses radio waves for long-range detection.
Why is LiDAR better than photogrammetry in some cases?
LiDAR offers higher accuracy and can detect ground surfaces beneath vegetation.
What industries benefit from LiDAR drones?
Surveying, construction, forestry, agriculture, mining, infrastructure inspection, and urban planning.
Read Our Other Blogs

16 February 2026
What Is Right of Way (ROW) in Drone Operations?
What Is Right of Way (ROW) in Drone Operations? In recent years, the recent spike in drone commercial operations has...

16 February 2026
When Do You Need Professional Drone 3D Scanning Services?
When Do You Need Professional Drone 3D Scanning Services? What Is the Difference Between DIY Drone Mapping and Professional Drone...

16 February 2026
Construction Site Drone 3D Scanning: From Progress Tracking to Quantity Surveys
Construction Site Drone 3D Scanning: From Progress Tracking to Quantity Surveys Why Construction Sites Use Drone 3D Scanning Construction site...

13 February 2026
How Drones Are Transforming Renewable Energy Inspection and Monitoring
How Drones Are Transforming Renewable Energy Inspection and Monitoring TL;DR Drones eliminate the need for manual climbing, significantly reducing workplace...

13 February 2026
Point Clouds, DEMs, and Orthomosaics: What Drone 3D Scanning Actually Delivers
Point Clouds, DEMs, and Orthomosaics: What Drone 3D Scanning Actually Delivers What Is Point Cloud in Drone 3D Scanning? A...

13 February 2026
How Drone Photogrammetry and LiDAR Work Together in 3D Scanning
How Drone Photogrammetry and LiDAR Work Together in 3D Scanning What Is Drone Photogrammetry and How Does It Create 3D...