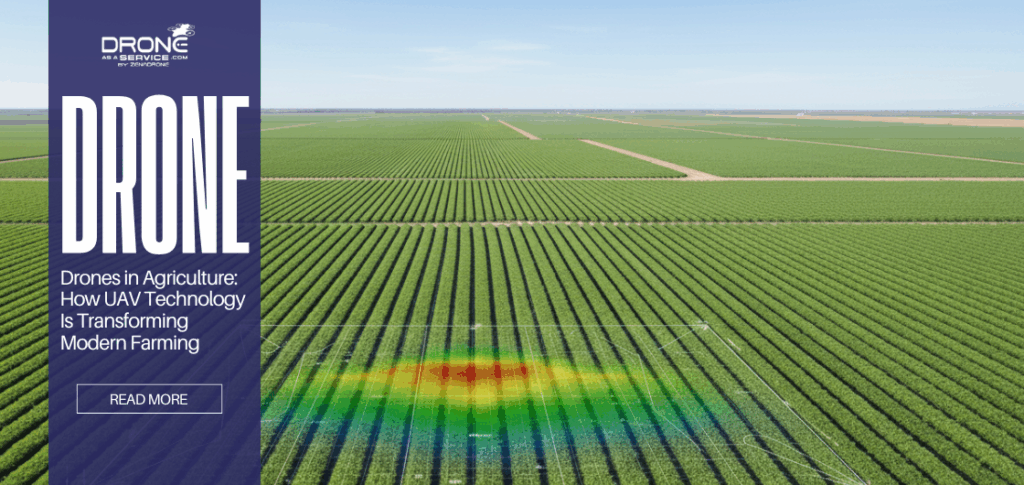
Drones in Agriculture: How UAV Technology Is Transforming Modern Farming

Introduction to Drones in Agriculture
Agriculture is undergoing a quiet but powerful transformation. Farmers are no longer relying only on traditional field inspections, manual spraying, or historical yield data. Instead, drones in agriculture are enabling faster decisions, higher precision, and more sustainable farming practices. From small family farms to large agribusinesses, UAV technology is becoming a practical tool rather than a future concept.
Driven by rising input costs, labor shortages, and the need for sustainable production, agricultural drones are now being used to monitor crops, analyze soil conditions, manage irrigation, and apply inputs with extreme accuracy.
What Are Agricultural Drones?
Agricultural drones, also known as farming UAVs, are unmanned aerial vehicles equipped with advanced sensors and imaging systems designed specifically for farm operations. These drones fly over fields to collect high-resolution data that would otherwise take days or weeks to gather manually.
Unlike conventional methods, drones provide a bird’s-eye view of the entire field, allowing farmers to identify issues early and act before problems spread.
Types of Drones Used in Agriculture
Multirotor Drones
Multirotor drones are the most commonly used drones in agriculture. They can hover, fly at low altitudes, and perform precise maneuvers.
-
Ideal for crop monitoring and precision spraying
-
Suitable for small to medium-sized farms
-
High accuracy but limited flight time
Fixed-Wing Drones
Fixed-wing drones are designed for covering large areas efficiently.
-
Best for large-scale mapping and surveying
-
Longer flight time and greater coverage
-
Less suited for spraying due to limited hovering ability
Drone Size, Payload & Capability Comparison
Different farming tasks require different drone capabilities. Payload capacity determines whether a drone can carry spray tanks, multispectral sensors, or thermal cameras. Flight time and coverage area directly impact operational efficiency, especially on large farms.
Core Applications of Drones in Agriculture
Crop Monitoring & Health Assessment
One of the most valuable uses of drones in agriculture is real-time crop monitoring. Drones can detect plant stress, nutrient deficiencies, pest infestations, and disease symptoms long before they are visible from the ground. Early detection helps farmers reduce losses and protect yields.
NDVI & Multispectral Imaging
NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index) and multispectral imaging allow farmers to assess plant health scientifically. These technologies highlight variations in crop vigor, helping farmers identify underperforming zones and take corrective action with precision.
Soil & Field Mapping
Drones create detailed 3D maps of fields, revealing elevation changes, drainage patterns, and soil variability. This data supports better land preparation, planting strategies, and long-term soil management.
Precision Spraying (Fertilizers, Herbicides & Pesticides)
Agricultural spray drones apply inputs only where needed. Instead of blanket spraying, farmers can target specific zones, reducing chemical use, lowering costs, and minimizing environmental impact.
Irrigation & Water Management
Thermal and multispectral sensors help identify moisture stress in crops. Farmers can adjust irrigation schedules based on actual field conditions rather than assumptions, improving water efficiency.
Planting & Seeding with Drones
Drone-based seeding is an emerging technology, particularly useful in hard-to-reach or erosion-prone areas. While still developing, it shows strong potential for reforestation and specialty crops.
Livestock Monitoring & Farm Surveillance
Drones are also used to monitor livestock, inspect fencing, and enhance farm security. Large ranches benefit significantly from aerial visibility and reduced manual labor.
Technology Behind Agricultural Drones
Modern agricultural drones combine hardware and software to deliver actionable insights. Sensors such as RGB, multispectral, and thermal cameras capture field data, while AI-powered software analyzes patterns and generates recommendations. Autonomous flight planning allows drones to operate efficiently with minimal human intervention, integrating seamlessly with farm management systems.
Benefits of Using Drones in Agriculture
-
Improved efficiency and time savings
-
Reduced input costs for water, chemicals, and labor
-
Higher crop yields through data-driven decisions
-
Enhanced environmental sustainability
-
Improved safety by reducing manual field exposure
Drones help farmers do more with fewer resources while maintaining high production standards.
Regulations & Legal Requirements for Agricultural Drones in the USA
In the United States, agricultural drone operations must comply with FAA regulations. Most commercial farming applications require FAA Part 107 certification. Operators must follow airspace restrictions, safety guidelines, and specific rules for spray drones. Compliance ensures safe integration of drones into national airspace while protecting people and property.
Adoption Trends & Market Growth of Drones in Agriculture
The adoption of drones in agriculture continues to grow as technology becomes more affordable and accessible. Improvements in battery life, payload capacity, and analytics software are accelerating adoption. Service-based drone models are also lowering entry barriers for farmers who prefer not to invest in equipment ownership.
Challenges & Limitations of Using Drones in Agriculture
Despite their benefits, agricultural drones come with challenges. Initial costs, training requirements, regulatory complexity, and weather dependency can limit adoption. Data interpretation also requires expertise to ensure insights are translated into effective farm actions.
Drone as a Service (DaaS) for Agriculture
Drone as a Service (DaaS) allows farmers to access advanced drone technology without owning or maintaining equipment. Service providers handle operations, compliance, and data analysis. This model is especially attractive for farms seeking cost-effective, scalable, and professional drone solutions.
Sustainability & Environmental Impact of Agricultural Drones
Drones support sustainable farming by reducing chemical runoff, optimizing water use, and lowering fuel consumption associated with traditional machinery. Precision application protects ecosystems while improving farm productivity.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How accurate are drones in agriculture?
With technologies like RTK and NDVI imaging, agricultural drones can achieve centimeter-level accuracy.
Are drones legal for farming in the US?
Yes, provided operators follow FAA regulations and obtain required certifications.
How much do agricultural drones cost?
Costs vary widely, but service-based models significantly reduce upfront investment.
Can drones really increase crop yield?
Yes, by enabling early detection of issues and precise input management.
Is Drone as a Service (DaaS) better than owning a drone?
For many farms, DaaS offers better flexibility, lower costs, and professional expertise.
Conclusion - The Future of Drones in Agriculture
Drones are no longer experimental tools in agriculture. They are becoming essential components of modern farming strategies. As technology advances and service models expand, drones will continue to drive efficiency, sustainability, and profitability across the agricultural sector.
Read Our Other Blogs
14 January 2026
Drone SLAM: Simultaneous Localization and Mapping
Drone SLAM: Simultaneous Localization and Mapping Imagine flying a drone in a dark tunnel, and the GPS signal is just...

13 January 2026
RF Drone Detection: How It Tracks and Identifies UAVs
RF Drone Detection: How It Tracks and Identifies UAVs In today’s market, commercial, industrial, and governmental operations have undergone significant...

12 January 2026
How Much Weight Can Drones Carry? | Ultimate Guide
How Much Weight Can Drones Carry? Drones were largely used for years as a hobby for photography and videography, but...

09 January 2026
Drone Surveying Explained: Faster, Safer & More Accurate Land Surveys
Drone Surveying Explained: Faster, Safer & More Accurate Land Surveys Introduction to Drone Surveying Drone surveying has rapidly become a...

08 January 2026
What Is LiDAR Archaeology & How Drone LiDAR Works to Reveal Hidden Sites
LIDAR Archaeology: How Drone LiDAR Reveals Hidden Ancient Landscapes TL;DR Drone LiDAR archaeology reveals ancient landscapes hidden beneath dense forest...

02 January 2026
Drone Mapping Explained: How Aerial Mapping & LiDAR Create Accurate Data
Drone Mapping Explained: How Aerial Mapping & LiDAR Create Accurate Data Drone mapping has transformed how industries capture, analyze, and...