Types of Drones and UAVs
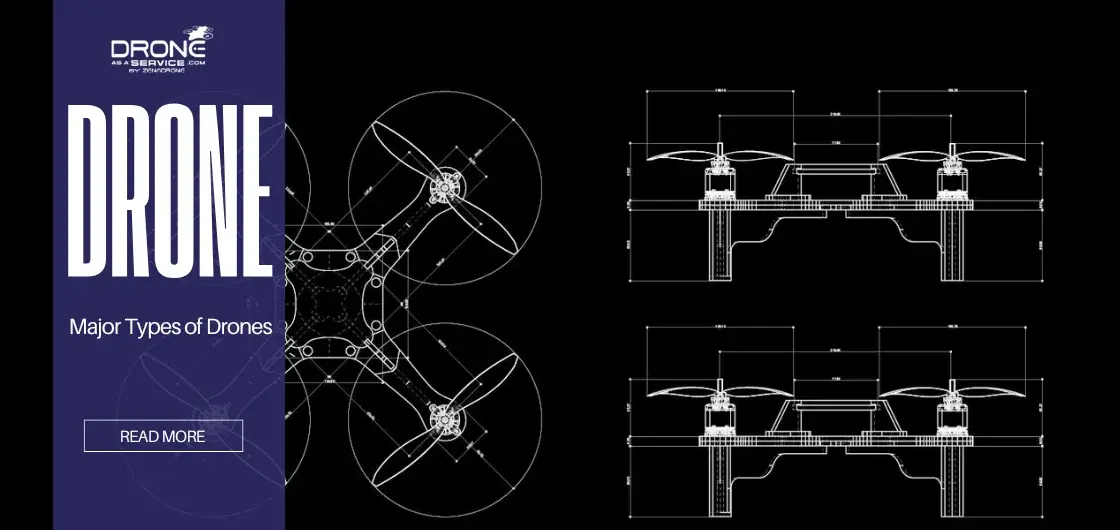
With drones changing the world in which we live, it is critical to learn about the various types of drones that business people and hobbyists can utilize. Every distinct category in the market is helpful for different purposes, and knowing the differences will enable you to choose the most appropriate aircraft.
This guide discusses the different types of drones, including their main characteristics in terms of structure, size, and range. Another aspect that we examine is payload capacity and power sources to describe the type of drones straightforwardly and understandably. Now we should have a look at the world of unmanned aerial technology.
Introduction
As the drone industry is growing at a very high rate, finding the appropriate model can be very confusing to new entrants in the market.
Drones are designed to accomplish particular tasks, so a racing drone cannot be used in agricultural mapping, and a bulky drone, in a similar manner, cannot be used indoors.
We shall divide the main factors that characterize these aircraft:
- Structure: The way the drone is physically constructed.
- Size: Dimensions and weight of unit.
- Range: The distance which it can cover when not connected to the controller.
- Payload: Its carrying capacity.
- Power Source: What is the source of power that runs the motors?
What Is a Drone?
A drone can be referred to as a UAV (Unmanned Aerial Vehicle). It is a plane that does not have a human pilot on board, in which complex aerodynamic principles are applied.
How Drones Work
Drones rely on lift, navigation, and precise controls to fly. The flight controller acts as the brain of the system and processes data to keep the aircraft stable.
Key Components
Several parts make a drone function correctly:
- Motors: These spin the propellers to generate lift.
- Propellers: They push air downwards to lift the drone.
- Sensors: These detect obstacles and ensure flight stability.
- GPS: This module provides positioning and navigation data.
- Battery: It powers all electronic components and motors.
Major Types of Drones (Structural Classification)
The physical structure is the most common way to categorize different kinds of drones. The frame dictates how the drone flies and its aerodynamic capabilities.
| Drone Type | Best For | Flight Time | Range | Payload Capacity | Cost Level | Skill Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multi-rotor | Photography, Inspection | Short (20–40 min) | Short | Medium | Low to High | Low |
| Fixed-wing | Mapping, Agriculture | Long (2+ hours) | Long | Medium | Medium/High | Medium |
| Single-rotor | Heavy Lifting, Hovering | Medium | Medium | High | High | High |
| Hybrid VTOL | Versatility, Cargo | Long | Long | Medium | High | Medium |
Multi-Rotor Drones
Multi-rotor drones are simple to operate and can hover at one point with four to eight propellers. It renders them ideal for inspection, although battery consumption is faster due to the continual use of the motor.
Fixed-Wing Drones
The fixed-wing drone resembles an airplane and provides standard wings as its means of lift, which makes it very efficient. It covers long distances smoothly, and it is ideal for mapping activities. However, it is not capable of flying around.
Single-Rotor Helicopter Drones
These drones resemble the appearance of little helicopters and have a large central rotor that is highly efficient and durable. They have heavy loads and make long flights on gas engines. They, however, need advanced training and skill to operate them.
Fixed-Wing Hybrid VTOL Drones
The Hybrid VTOL (Vertical Take-Off and Landing) drones take off directly into the air in helicopter mode and then switch to plane mode to proceed forward. This design offers the freedom of hovering and the efficiency of a fixed-wing aircraft. They are used more and more in industries such as commercial delivery.
Types of Drones According to Their Sizes
Size is a critical factor when discussing drone classifications. The size often dictates legal regulations and portability.
| Size Category | Typical Weight | Flight Time | Range | Main Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nano | < 100g | 5–10 mins | Very Short | Fun, Indoor play |
| Micro | 100g – 250g | 10–20 mins | Short | Racing, Hobby |
| Mini | 250g – 2kg | 20–30 mins | Medium | Photography, Travel |
| Small | 2kg – 25kg | 30–45 mins | Medium | Commercial Inspection |
| Medium | 25kg – 150kg | 1–2 hours | Long | Logistics, Agriculture |
| Large | 150kg – 600kg | Hours | Very Long | Military, Transport |
| Heavy-lift | > 600kg | Hours | Global | Cargo, Defense |
Nano Drones (Under 250g)
Nano drones are the miniature insects in the drone world. They are easily portable in the palm of your hand. They are primarily applied to indoor entertainment.
Micro Drones
Micro drones are bigger and portable. They are trendy among first-time users and children because of their safety.
Mini Drones
Mini drones bridge the gap between toys and tools. Many professional photographers use high-end mini drones because they are easy to transport to remote locations.
Small Commercial Drones
These are the workhorses of the industry, which carry better sensors and cameras. You often see them inspecting roofs or towers.
Medium Drones
Medium drones are designed to work on heavy-duty tasks. They are equipped with specialized gear, such as LIDAR scanners, and are commonly used in agriculture and search and rescue.
Large / Heavy-Lift Drones
These are similar to small crewed aircraft. These drones’ main application is in complex logistical challenges since they can carry heavy loads within cities.
Types of Drones According to Their Range
The range is used to calculate the distance between the pilot and the drone. This range is essential for drone types that are employed in surveillance.
| Range Category | Range Distance | Flight Duration | Ideal Applications | Industry Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Short-range | < 2 km | 15–20 mins | Selfies, Spot check | Real Estate |
| Mid-range | 2 km – 10 km | 30–50 mins | Mapping, Scouting | Security |
| Long-range | 10 km – 100 km | 1–3 hours | Pipeline monitoring | Energy |
| BVLOS | > 100 km | 4+ hours | Long-haul cargo | Logistics |
Short-Range Drones
These utilize Wi-Fi or simple radio connections. They are intended for visual line-of-sight flying and are great for close-up inspections.
Mid-Range Drones
Mid-range units use advanced transmission systems to explore large properties without signal loss. They are standard for commercial mapping projects.
Long-Range Drones
These are often fixed-wing aircraft that patrol borders or power lines effectively. They transmit data over vast distances.
BVLOS (Beyond Visual Line of Sight) Drones
BVLOS represents the future of drone operations, as these flights require special government permits.
Types of Drones According to Their Power Sources
How a drone stays powered impacts its utility and endurance.
| Power Type | Efficiency | Flight Time | Maintenance | Best Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Battery | High | Low / Medium | Low | Consumer, Commercial |
| Fuel-powered | Medium | High | High | Agriculture, Industrial |
| Solar | High | Very High | Medium | Surveillance |
| Hybrid | High | High | High | Cargo, Transport |
Battery-Powered Drones
Lithium-polymer (LiPo) batteries are the industry standard. They are clean, quiet, and easy to recharge. However, they limit flight times mostly to under an hour.
Fuel-Powered Drones
(Gasoline/Hybrid Engines)
Gas engines provide immense energy density. They enable the drones to travel long distances. In addition, they are loud and have to maintain engines.
Solar-Powered Drones
These drones possess solar cells in their wings. They can fly during the day for extended periods and are mainly used for environmental monitoring.
Hydrogen Fuel Cell Drones
Hydrogen offers clean energy with long endurance. These cells generate electricity to power electric motors. They are becoming popular for long-range inspection.
Types of Drones According to Their Motors
The motor is the heart of propulsion and affects drone efficiency.
| Motor Type | Efficiency | Durability | Noise Level | Best Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brushed | Low | Low | Medium | Toys, Nano drones |
| Brushless | High | High | Low | Photography, Racing |
Brushed Motor Drones
Brushed motors are inexpensive and are easy to make. It is spun with the assistance of physical brushes.
Brushless Motor Drones
Brushless motors are more powerful and efficient because they take a much longer time since there is no friction. This technology is employed on most commercial drones.
Single-Rotor Motor Systems
This system employs a single significant motor lift. It is energy efficient and mechanically complex, and copes with the wind better than multi-rotors.
Multi-Rotor Motor Systems
These systems have a combination of several motors. The flight controller directly controls the speed of each motor and enables unbelievable stability and manoeuvrability.
Choosing the Right Drone Type
With so many drone types, choosing is hard. You must evaluate your specific needs carefully.
- Purpose: Are you taking photos or inspecting crops? Your goal dictates the drone you need.
- Flight Time: Do you need to fly for 20 minutes or two hours? Battery life is a significant constraint.
- Budget: Drones range from $50 to $50,000. Know your financial limit before shopping.
- Payload Needs: Must you carry a heavy camera? Ensure the drone can lift your required gear.
- Regulations: Laws vary by weight and location. Always check local aviation rules before flying.
- Experience Level: First-time fliers must settle for smaller and safer quadcopters. Enterprises should invest in reliable and specialised platforms.
Conclusion
We have examined a large number of types of drones. From nano toys to heavy-lift giants, the options are endless. Drone classifications help buyers make informed decisions. Whether for fun or business, there is a drone for you.
These classifications are what you need to know so that you can choose the correct tool. Always consider range, size, and power source. The drone industry continues to innovate rapidly.
Read Our Other Blogs

28 January 2026
Drone Mapping Failures You Must Avoid for Accurate and Reliable Results
Drone Mapping Failures You Must Avoid for Accurate and Reliable Results Drone mapping is changing the world. It aids surveying,...
26 January 2026
Types of Drones and UAVs
Types of Drones and UAVs With drones changing the world in which we live, it is critical to learn about...

23 January 2026
Aerial Data Collection: How Drones Are Transforming Data Capture and Analysis
Aerial Data Collection: How Drones Are Transforming Data Capture and Analysis Introduction: When Data Needs a Higher Perspective When data...
21 January 2026
Drone Inspection Guide: Safer Inspections for Hard-to-Reach Areas
Drone Inspection Guide: Safer Inspections for Hard-to-Reach Areas Introduction Drone inspection has transformed how industries inspect assets that are difficult,...

21 January 2026
PPK Workflow for Drones: Complete Process & Accuracy
PPK Workflow for Drones: Complete Process & Accuracy Drone operators aren’t the only ones concerned with accuracy for any project....

20 January 2026
Altitude Hold Technology in Drones: Stability, Control, and Flight
Altitude Hold Technology in Drones: Stability & Control Before technological developments, drones were viewed as niche gadgets. Today, it is...