Aerial Data Collection: How Drones Are Transforming Data Capture and Analysis
When data is collected from the ground, it often comes with blind spots. Physical access can be limited, environments can be hazardous, and traditional surveys can be slow or expensive. This is where aerial data collection changes the equation.
By capturing information from above, organizations gain a clearer, more comprehensive view of assets, land, and infrastructure. Over the years, data captured from the air has evolved from relying heavily on satellites i.e, Google earth and manned aircraft to a more agile, precise approach powered by drones.
Today, drones are redefining how aerial data is collected, processed, and analyzed. They make it possible to gather high-resolution data quickly, safely, and cost-effectively, especially for industries that depend on accurate, timely insights to make critical decisions.
In this guide, we’ll walk through:
- What aerial data collection really means
- How aerial data collection and analysis actually works
- Why drones have become the dominant solution
- Real-world drone use cases across industries
- Aerial forensic data collection explained
- Where aerial data collection is heading next
Let’s deep dive with a simple definition.
What Is Aerial Data Collection?
Most people imagine satellites when they hear “aerial data collection.” That’s not wrong but it’s only part of the story. In reality, aerial data can be captured from multiple heights, using different platforms, each designed for a very specific purpose.
However, modern aerial data collection increasingly relies on low-altitude platforms that offer greater control and precision. These platforms include drones, also known as unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs).
While satellites provide broad coverage and aircraft handle regional surveys, drone-based aerial data collection fills the critical gap between scale and detail. Drones can fly lower, capture sharper data, and be deployed on demand—making them ideal for commercial and industrial applications.
You may like also: How Drones and Cloud Platforms Work Together for Real-Time Data Insights
How Aerial Data Collection and Analysis Works
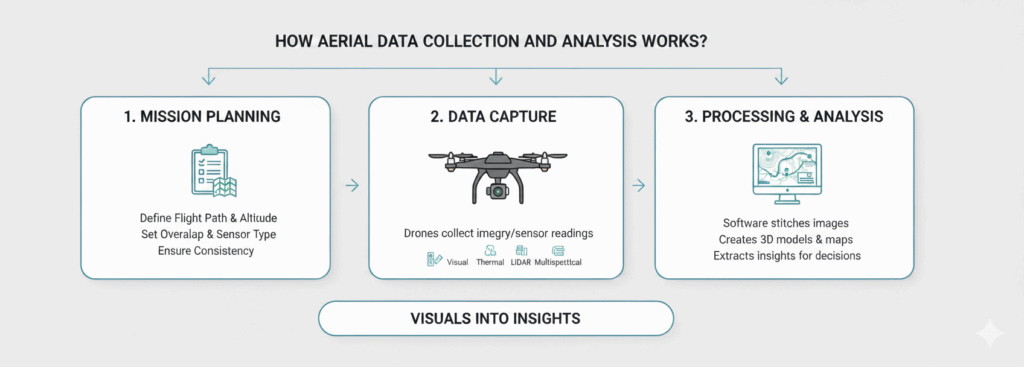
Capturing aerial data is easy. Turning it into something you can actually make decisions from that’s where the real work begins.
First Step
The process typically begins with mission planning. Flight paths, altitude, overlap, and sensor selection are carefully defined based on the type of data required. This planning stage ensures consistency and accuracy.
Second Step
Next comes data capture. Drones collect images or sensor readings while following pre-programmed routes. Depending on the mission, this may include standard visual imagery, thermal data, LiDAR scans, or multispectral information.
Third Step
Once captured, the data moves into processing and analysis. Specialized software stitches images together, creates 3D models, generates maps, or extracts measurements. This stage is where data captured from the air and analysis truly deliver value transforming visuals into insights that support decisions, inspections, or investigations.
Why Drones Dominate Modern Aerial Data Collection
The question is no longer whether drones can collect aerial data? The real question is why so many industries stopped using anything else?
In today’s commercial landscape, drones have become the preferred platform for aerial data collection and for good reason.
Drones operate at lower altitudes, allowing them to capture highly detailed data that satellites and aircraft often miss. They can be launched quickly, fly precisely, and revisit the same area repeatedly for comparison over time.
Cost efficiency is another key factor. Compared to manned aircraft, drones require less logistics, less fuel, and fewer personnel. This makes frequent data collection financially viable rather than an occasional expense.
Most importantly, drones improve safety. Inspections and surveys that once required people to work at height or in hazardous environments can now be performed remotely, without exposing personnel to unnecessary risk.
Imagine! If you’re responsible for inspecting assets, planning a site, or documenting conditions, this level of visibility changes how you work.
Anyhow, in practical terms, drones are no longer just one option for data captured from the air, they are the default solution for many modern use cases.
Types of Data Collected Using Drones
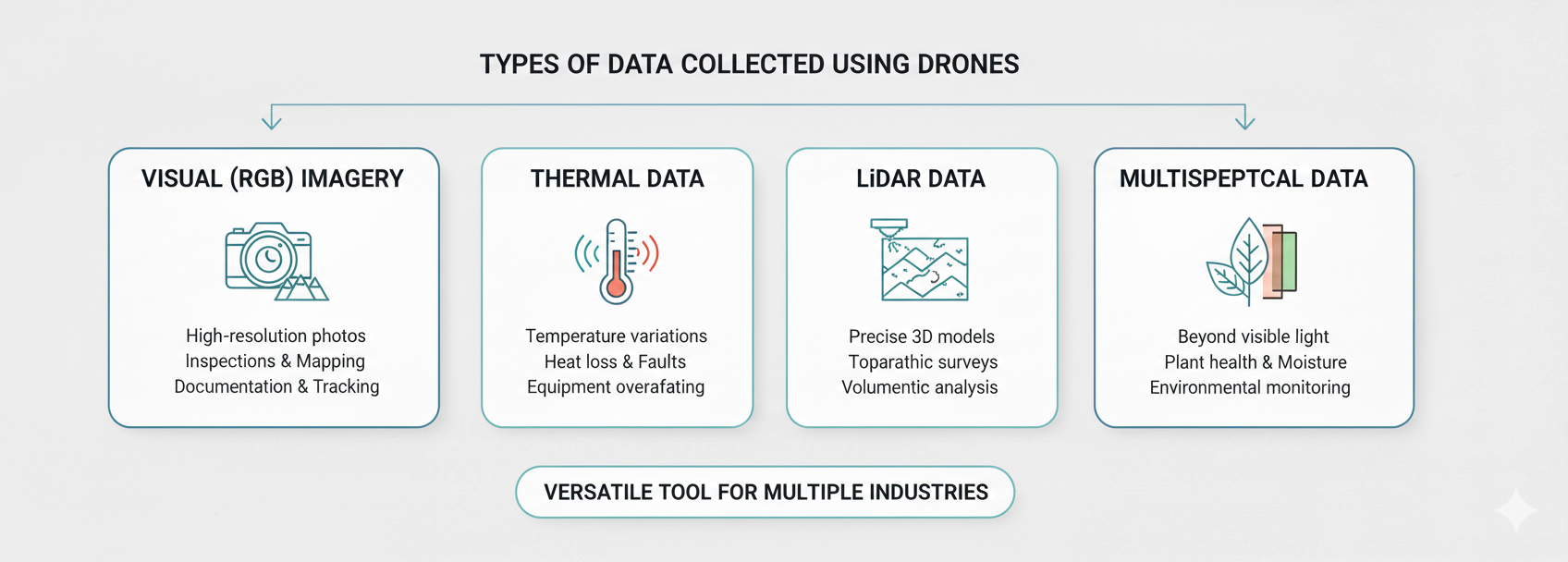
Drone-based aerial data collection supports a wide range of data types, each serving different analytical needs.
Visual (RGB) imagery is the most common. High-resolution photos are used for inspections, mapping, documentation, and progress tracking.
Thermal data reveals temperature variations. This is especially valuable for identifying heat loss, electrical faults, or equipment overheating that may not be visible to the naked eye.
LiDAR data uses laser pulses to create precise 3D representations of terrain and structures. It is particularly useful for topographic surveys, volumetric measurements, and vegetation analysis.
Multispectral data captures information beyond visible light. In agriculture and environmental monitoring, this data helps assess plant health, moisture levels, and land conditions.
Together, these data types make drones a versatile tool for data collection and analysis across multiple industries.
If you take interest in agriculture and environmental monitoring, you may like to read: Drone Technology: Reshaping The Future Of Environmental Management
Aerial Data Collection Drone Use Cases Across Industries
Drone-based aerial data collection is now embedded across a wide range of sectors.
In construction and infrastructure, drones provide accurate site maps, monitor progress, and identify issues early, reducing delays and rework.
The energy and utilities sector relies on drones to inspect power lines, wind turbines, solar farms, and pipelines. Aerial data helps detect faults before they lead to costly failures.
In agriculture, data captured from the air supports precision farming. Farmers use drone data to optimize irrigation, detect crop stress, and improve yields.
Mining and quarrying operations use drones to measure stockpiles, assess site safety, and plan excavation activities with greater accuracy.
For insurance and asset assessment, drones enable rapid documentation after incidents, supporting claims processing and risk evaluation.
Across all these industries, the common thread is the need for accurate, timely, and repeatable data, something drones are uniquely positioned to deliver.
Aerial Forensic Data Collection: When Accuracy Matters Most
Aerial forensic data collection is a specialized application where accuracy, documentation, and traceability are critical.
When timelines are tight and details matter, aerial data collection stops being about efficiency and starts being about accuracy.
This approach is often used for accident reconstruction, disaster assessment, and legal investigations. Drones capture high-resolution, time-stamped data that preserves conditions as they exist at a specific moment.
Because drones collect data without disturbing the scene, they are ideal for forensic applications. The resulting models and maps can be analyzed, archived, and presented as visual evidence to support investigations or legal proceedings.
Read also: Drone Solution: A Technological Aid for Disaster and Rescue Operations
In scenarios where details matter and margins for error are minimal, drone-based aerial forensic data collection offers a level of precision that traditional methods struggle to match.
One thing becomes clear: aerial data collection is no longer about flying higher; it’s about seeing smarter.
Benefits of Drone-Based Aerial Data Collection
The advantages of using drones extend beyond convenience.
Drone data enables faster decision-making by delivering insights quickly, often within hours rather than weeks.
It significantly reduces human risk by minimizing the need for personnel to access dangerous or hard-to-reach locations.
Drone operations are scalable and repeatable, making it easier to track changes over time and maintain consistent data quality.
Perhaps most importantly, drone-based aerial data collection improves long-term planning by providing reliable data that organizations can trust.
How drones inspect. If you are interested in it, read here: Drone Inspection Guide: Safer Inspections for Hard-to-Reach Areas
Challenges and Limitations of Aerial Data Collection
Despite its advantages, aerial data collection is not without challenges.
Weather conditions can affect flight operations and data quality. Regulatory requirements vary by region and must be carefully followed. Additionally, collecting data is only part of the equation processing and interpreting that data requires expertise and the right tools.
These factors are why many organizations choose to work with experienced aerial data collection providers who understand both the technology and the regulatory landscape.
The Future of Aerial Data Collection and Analysis
The future of data captured from the air lies in automation and intelligence. Advances in artificial intelligence are accelerating data analysis, allowing insights to be extracted faster and more accurately.
Autonomous drone operations are reducing the need for manual control, while real-time data transmission is enabling faster responses in critical situations.
As these technologies mature, aerial data collection and analysis will become even more integrated into everyday decision-making across industries.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is aerial data collection the same as drone mapping?
Drone mapping is one application of aerial data collection. Aerial data collection is broader and includes inspections, analysis, and forensic documentation.
How accurate is drone-based aerial data collection?
Accuracy depends on sensors, flight planning, and processing methods, but modern drone systems can achieve very high precision.
Is aerial forensic data collection legally acceptable?
When conducted properly, drone data is widely used for documentation and analysis. Legal acceptance depends on local regulations and data handling practices.
What affects the cost of aerial data collection?
Factors include area size, data type, complexity, and processing requirements.
How long does aerial data analysis take?
Timelines vary, but many drone-based projects deliver usable insights within days rather than weeks.