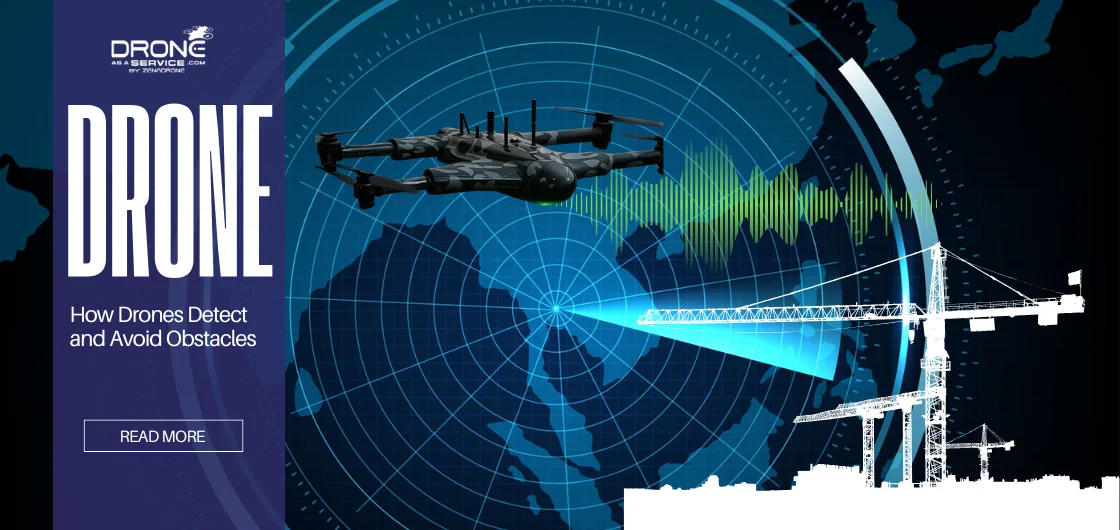
How Drones Detect and Avoid Obstacles
Drones are rapidly becoming essential tools for surveying, inspection, and delivery, thanks to major advancements in autonomous flight. A key innovation driving this growth is obstacle avoidance technology—an intelligent “sixth sense” that helps drones detect and navigate around potential hazards. This capability improves safety, reduces crash risks, and enables reliable operation across complex environments.
This article explores why obstacle avoidance matters, where it’s applied, and how the underlying detection systems work.
How Drones Detect and Avoid Obstacles
Recently, there has been a rapid adoption of drones across many different industries. Continued innovations have pushed drones through transformative breakthroughs, allowing them to become practical tools for surveys, inspections, and deliveries.
One of these developed technologies is the obstacle avoidance feature, which addresses the concern of collisions and crashes that come with flying a drone. You could call it a “sixth sense,” providing autonomous awareness to the drone to avoid hitting objects in its way.
This article looks into obstacle avoidance in drones–why it matters, where it’s useful, and how exactly it works.
What Is Obstacle Avoidance in Drones?
In simple terms, obstacle avoidance refers to the drone’s capability to sense, analyze, and go around obstacles in its path. Using sensors, the drone detects obstructions in its surroundings and steers away from them, maintaining a stable and safe flight performance.
- How does a drone recognize obstacles around it?
- What triggers the drone to change its path or altitude?
- How does real-time sensing prevent collisions during flight?
Older drone models needed pilots to control them manually and watch out for things like power lines, walls, buildings, and trees. This was especially risky when flying far or through tight spaces.
Newer drones have sensors that let them detect and avoid obstacles on their own. This real-time awareness helps them make quick, smooth moves that even skilled pilots might miss.
Suppose a drone is inspecting a towering wind turbine. As it elevates, the drone constantly scans for trees, power lines, and moving blades, using specialized sensors and a high-resolution camera. Systems like the Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) help maintain balance and precise movement during these adjustments. When something enters its flight path, the drone automatically adjusts its direction, speed, and altitude to avoid collision.
Why Obstacle Avoidance Matters
Every drone flight carries a risk of collision and crashes. A single mishap may damage or completely compromise the unit. This results in not just costly repairs but also unwanted downtime and headaches.
Here’s what drone avoiding obstacles provides as an essential safety measure:
Prevents Crashes and Equipment Damage
Collisions can only mean one thing: hefty expenses. Repairing cameras, sensors, gimbals, and hardware can easily cost hundreds of dollars. And if you’re unfortunate, heavy damage can go up to the thousands.
That’s why responsible drone pilots always put safety first. Obstacle avoidance helps by automatically spotting obstacles and steering the drone away from them. This is especially important in search and rescue, infrastructure, and energy monitoring.
Improves Safety in Crowded or Complex Environments
Crowded and complex settings are filled with physical obstructions. Crashing here poses risks not only to the drone but also to people and property. In this challenging environment, obstacle avoidance becomes a necessity, as it ensures safe and smooth navigation through tight spaces.
Enables Autonomous Missions
Obstacle avoidance is a foundational instrument for greater autonomy, which empowers BVLOS operations, precision mapping, timely delivery services, and efficient inspections.
Where Drone Obstacle Avoidance Is Used
Drone obstacle avoidance is a powerful feature that improves safety, efficiency, and reliability in every drone operation. So naturally, it has a wide variety of practical applications, indoor and outdoor, in different industries.
Indoor Applications
- Warehousing and Inventory Management: Inside massive distribution centers, drones can navigate aisles and racks without crashing to perform various tasks in AI-driven drone inventory management.
- Factories and Industrial Plants: In a setting where collisions can force operational shutdowns, obstacle avoidance helps drones safely navigate in tight spaces with machines.
- Indoor Inspections: Obstacle avoidance makes drone inspections in tunnels, pipelines, and power plants safer, even when the GPS signal is lost.
- Research and Education: Educational applications enable hands-on learning for students, while research allows testing robotics and navigation in controlled spaces to explore and push the limits of obstacle avoidance.
Outdoor Applications
- Delivery Drones: Equipped with obstacle avoidance, drones can fly through urban areas to deliver parcels and medical supplies, avoiding trees, buildings, and power lines in cities.
- Agriculture: Obstacle avoidance enables drones to fly near crops and avoid farm machinery, delivering more efficient coverage and reducing the risk of damage.
- Construction and Mining: In these industries, physical obstructions are everywhere, like cranes, trucks, and rugged terrain. Drones with obstacle avoidance can navigate through these spaces to capture data without any problem.
- Public Safety and Search and Rescue: Drones help first responders locate people in forests, collapsed structures, or disaster zones, where drone-as-a-first-responder programs enable rapid assessment before ground teams arrive. Obstacle detection keeps these missions safe and fast.
- Oil and Gas, Energy Inspections: Obstacle avoidance is vital for precise flights around rigs, flare stacks, and transmission lines in energy environments.
How Drones Detect Obstacles
To avoid obstacles, the drone needs to detect them first–fast and accurately. But the question is, how do drones detect obstacles? Well, they use a combination of high-resolution cameras and specialized sensors that function as their eyes and ears.
| How Drones Detect Obstacles | Description |
|---|---|
| Ultrasonic Sensors | Measure distance to objects using sound waves that bounce back. |
| Infrared Sensors | Detect objects via reflected IR light and trigger a drone response. |
| Stereo Vision Cameras | Dual cameras enable depth perception for obstacle detection. |
| LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) | Uses laser pulses to create precise 3D maps, even in low light. |
| GPS & IMU | Provide positional awareness and stability, supporting obstacle avoidance. |
How Drones Avoid Obstacles
After the sensors and cameras detect obstacles, the drone then processes this information for quick decision-making and precise maneuvers. There are several ways drones avoid obstacles.
| How Drones Avoid Obstacles | Description |
|---|---|
| Reactive Avoidance | Instant rerouting to prevent collisions, similar to human reflexes. |
| Path Planning Algorithms | AI calculates the safest path in advance and adapts to changes. |
| SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) | Builds live 3D maps of the environment during flight. |
| Integration with Autonomous Navigation Systems | Combines sensor data, algorithms, and mapping for safer autonomous flight. |
Benefits of Obstacle Avoidance Systems
Obstacle avoidance detects and evades dangers in real-time, making every flight safer and more reliable. This autonomous capability translates to various benefits that further optimize drone operations.
Safer flights with reduced crash risk
Perhaps the most obvious benefit of drones avoiding obstacles is fewer collisions, safeguarding the drone and its payloads. This is particularly important for industries like construction, energy, and mining, where missions involve pricey attachments.
Better performance in delivery, inspection, and agriculture
Thanks to drone obstacle avoidance, drones can maximize safety, precision, and efficiency. With this improved performance, achieving mission success is as easy as it gets.
Enhanced ability to operate in GPS-denied areas
Some sites, like indoor warehouses, tunnels, mines, and industrial facilities, block satellite signals, disabling the GPS functionality. But with obstacle avoidance systems using LiDAR or SLAM, drones can maintain their own sense of direction in inaccessible areas and BVLOS operations.
Limitations and Challenges
Obstacle avoidance comes with great advantages. But it isn’t without any drawbacks.
- Higher cost of advanced drones: Advanced sensors like LiDAR and stereo cameras are expensive, making it difficult for small businesses or hobbyists.
- Sensor limitations in poor weather: Fog, rain, and low light affect the performance of cameras and sensors, leading to inaccurate readings and an increased risk of collisions. Under these conditions, the operator might need to step up in flying the drone.
- Processing power needed for real-time obstacle avoidance: As sensory data keep flooding in mid-flight, obstacle avoidance demands constant computing. This high processing load drains battery life, cutting down flight duration.
Future of Drone Obstacle Avoidance
Drone obstacle avoidance has yet to reach its full potential. Engineers and scientists are still seeking and making improvements. But one thing is for certain: the next chapters of drones equipped with obstacle avoidance technology look promising.
Here’s what you can expect from obstacle avoidance in the future:
- AI-powered predictive navigation that uses pattern recognition and machine learning to anticipate obstacles.
- Integration with swarm drone coordination, where every unit becomes part of a centralized intelligence network to avoid midair crashes and share data in real time.
- Improved sensors for all-weather operation that allow drones to safely and efficiently operate under harsh conditions.
- A critical role in urban air mobility, making air taxis and delivery drones a reality as a mode of transportation in the skies.
In the future, obstacle avoidance will seamlessly blend intuitive AI and smaller and smarter sensors and cameras. One day, they will move from simple navigation tools to autonomous aerial systems.
Conclusion
Obstacle avoidance is the backbone of safe, autonomous drone operations. Without it, drones can never be truly independent and instead stay reliant on human pilots.
But the evolution of drones alongside obstacle detection is inevitable, and they’ll surely become smarter, faster, and more reliable. By then, navigating crowded places, complex buildings, and confined spaces won’t be a problem. You can reduce risks, save costs, and ensure success across multiple industries without human intervention.
At Drone as a Service (DaaS), we bring drones engineered with reliable obstacle avoidance – the ZenaDrone 1000. From indoor applications like warehousing and industrial inspections to outdoor operations in delivery and agrarian surveys, the ZenaDrone 1000 transforms businesses in different sectors.