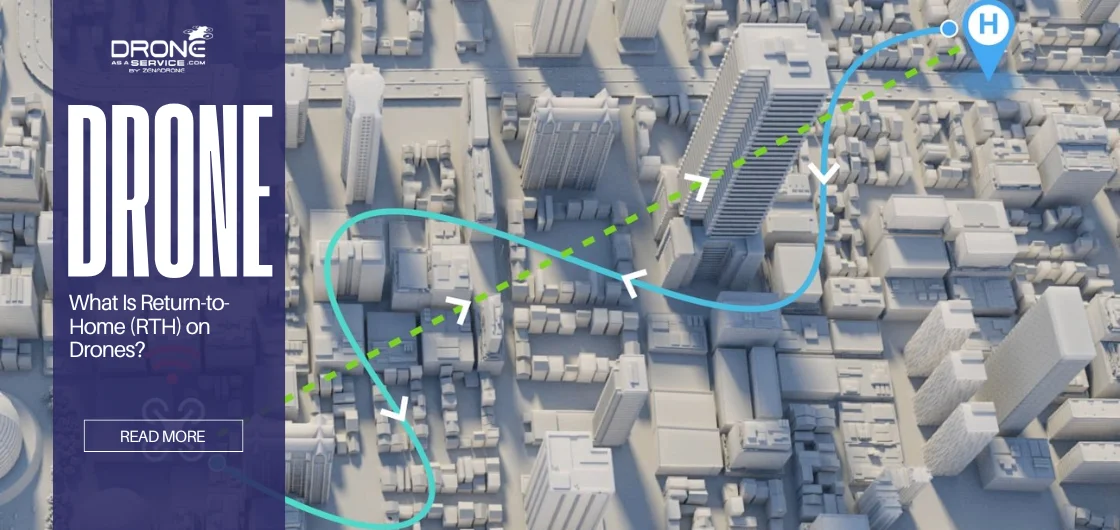
What Is Return-to-Home (RTH) on Drones?
The worst thing that could happen is losing an expensive drone while on a mission. Every pilot feels stressed out at the thought of taking off. The RTH feature on drones is a very important safety net, which is a good thing.
So, what does RTH mean? Return-to-Home is a smart safety feature. It will automatically return your unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) to its designated location. Specifically, it guides the Drone back to a set point that is its home. This happens when a serious emergency arises.
This feature is very important for all Drone as a Service (DaaS) businesses. It significantly reduces the risk of accidents and the permanent loss of assets. It is crucial to understand exactly how RTH works. Maintaining professional flight safety standards is important.
The ZenaDrone 1000 and IQ model is an example of a system that is more stable and has reliable RTH functions. For complicated industrial operations, they offer unmatched safety and accuracy.
In this blog article, we will examine the importance of this feature in detail. How it works and why it is the start of even more autonomous features that will be added in the future.
Understanding the Return-to-Home (RTH) Feature
The Return-to-Home (RTH) feature is a significant safety aspect of modern drones and a crucial security purpose of professional drone systems. It serves as a safety system of navigation that operates in the event of a high risk of losing the drone. It automatically lands the drone at the starting point.
It was designed to reduce the risk of crashing and protect expensive drone equipment. And the disappearance of the signal before RTH frequently led to failure.
In the present day, the characteristic demonstrates the extent to which drone automation has evolved. It transforms a drone into a serious work tool, rather than a toy. Early RTH systems were highly primitive, and they typically straightened back and ignored any obstacle.
Compare that to the smart systems that come with modern platforms. The IQ Nano features smart RTH, which helps newbie professionals fly with ease. The ZenaDrone 1000 utilizes AI to achieve advanced pathfinding, ensuring improved performance in challenging environments.
This advancement is the key to DaaS reliability. An effective return-to-home option is a professional standard.
How Does the Return-to-Home Function Work?
The RTH function is intelligent because it relies on core flight components working together. In particular, the GPS module, the compass, and the flight controller all work together perfectly.
This is a general step-by-step guide to how RTH works in most professional drones:
- Takeoff and GPS Lock: The drone notifies of an excellent GPS connection. It reserves the takeoff point as a permanent drone home point.
- RTH Activation: The drone first rises to a safe RTH height that has been set. This may occur when the pilot presses a button, the battery is low, or the signal is lost.
- Ascend/Adjust Altitude: The drone first rises to a safe RTH height that has been set. This helps it avoid obstacles like trees or tall buildings. If the drone is already flying at that height or higher, it stays at that height.
- Navigation Phase: The flight controller identifies the least distance to fly back home. It utilizes live GPS position and compass direction to determine the heading. The compass maintains a straight course for the Drone towards the home point.
- Obstacle Avoidance: Advanced return-to-home drones feature a sensor that monitors the path to prevent collisions. They change their flight path to avoid colliding with objects.
- Landing: If the drone is exactly at the home point, it initiates a controlled vertical descent.
The ZenaDrone 1000 is equipped with a multi-sensor GPS and AI-controlled stabilization software. This renders RTH more precise, which is also present in windy or weak-signal regions.
Types of Return-to-Home (RTH) Modes
Not all RTH activations function in the same manner. The mode of RTH that is used depends on the type of trigger. Professional pilots must be thoroughly familiar with these modes of operation. It helps you figure out how much control you have during the return sequence.
Here are the three main RTH modes commonly used in professional operations:
| RTH Mode | Trigger Type | Pilot Control Level | Reliability Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manual RTH | Pilot Command (Button / App) | High (Can usually be cancelled or overridden) | Convenience and pre-emptive safety |
| Failsafe RTH | System Activation (Lost Signal / Low Battery) | Low (System prioritized for critical safety) | Critical asset recovery and loss prevention |
| Smart RTH | Pilot Command / Advanced System | High (Intelligent path calculation) | Efficiency, speed, and RTH accuracy |
Triggers That Activate Return-to-Home
It is essential to understand the triggering factors that cause RTH, as this knowledge can be used to mitigate the risk of RTH. These are not system glitches. They are intended system responses. They are put in place to stop disastrous accidents from occurring.
The entire concept of RTH on drones revolves around foreseeing and preventing safety risks.
Low Battery Warnings
The most frequent is the low battery level. The drone constantly measures the battery voltage accurately. The system determines the amount of power required to return to its current position. It will always leave a margin of safe power to allow for a smooth return.
Lost Controller Signal
Professional DaaS drones rely on a robust radio connection for seamless operation. This connection is between the aircraft and the remote controller. If the drone flies beyond its optimal range of operation, the radio connection is lost. If the connection is broken due to electronic interference, RTH will activate.
Pilot Command (Manual Trigger)
The pilot can activate RTH at any location during the mission. It is employed if the pilot loses sight of the drone. It is also applied in cases of pilot spatial disorientation.
Restricted Airspace or Geofencing
Geofencing technology is available on many modern DaaS drones. This system utilizes GPS to enforce legal no-fly zones. If the drone flies into a restricted area by mistake, RTH may be activated automatically. This will avoid severe regulatory offenses and possible penalties.
How Drones Determine the Home Point
The most crucial data of the Return-to-Home (RTH) feature is the home point. Without it, RTH doesn’t work. The drone must return to a safe location in case of an emergency. Defining the home point:
Initial GPS Record
This point is typically the home point after takeoff of the drone. This can only occur when a GPS is well locked. GPS captures the position in terms of latitude, longitude, and altitude. It becomes the home of drones there.
Significance of GPS Calibration
GPS calibration is required before each flight. The pilots should wait until the app indicates to them that the home point has been set. The GPS will not be calibrated properly, resulting in incorrect coordinates, and the drone will return to the wrong position—a poor calibration leads to a very low RTH requirement for accuracy.
Dynamic Home points
In certain professional systems, the home point may be dynamic. It can be updated while the drone is in flight. For example, it can trail behind the pilot’s controller. This comes in handy when flying off a moving boat or car, so the drone returns to the exact point you are at.
Safety Advantages
Home points will ensure the drone will not be lost. They ensure that the landing path is safe and predictable. They eliminate the speculation of a critical failure. It is an aspect that safeguards costly equipment and valuable information.
You know, you can never exaggerate the fact that you must always make sure to set the home point correctly. This minimal step is the foundation of drone safety.
The Role of GPS and Compass in RTH Accuracy
The return to Home (RTH) system relies on its navigation sensors. The most important are the GPS and the compass, which should be coordinated and complementary to each other to maintain RTH.
GPS for Positioning
The US GPS satellites are not the only ones the drones use. Drones operated by professionals utilize more than one GPS, including Galileo (Europe), GLONASS (Russia), and BeiDou (China). The presence of a large number of systems provides additional backup through satellite systems. It assists the drone in achieving a precise position, which is essential for safe night drone flights. This accuracy is required to locate the home point.
Compass for Orientation
The compass will always inform the drone of its direction. It indicates the heading in relation to magnetic north. In RTH, it sends this direction data to the drone, enabling it to fly straight to home. In the event of a compass malfunction, the drone will lose its direction and fail to follow its designated route.
Warnings about interference
Interference is a significant problem for RTH’s ability to function effectively. The compass sensor can be seriously affected by strong magnetic interference. High-voltage power lines and big metal buildings are two examples of sources. They can also include big service vehicles. Buildings or thick foliage can completely block GPS signals by interfering with them. This interference makes RTH much less accurate and reliable.
Calibration and firmware
It is essential to keep both the GPS and compass systems up to date. To ensure that RTH functions properly, it is necessary to update the firmware regularly.
The compact IQ Nano, for example, has a high-tech dual-compass calibration system built in. This technology mitigates the effects of magnetic drift, which can cause problems. It was intentionally designed to be highly accurate and stable.
Environmental factors
These factors are also very important. Strong winds can easily throw off accuracy. The drone’s system has to fight against these outside forces constantly. It is working hard to stay on the planned path back to the drone’s home point.
Obstacle Avoidance and RTH Safety Enhancements
In the past, the concept of return-to-home (RTH) was simply a direct flight back home to the base. And that frequently resulted in crashing into walls or trees. Modern drones have solved this issue today. They automatically avoid obstacles. This is one of the major safety enhancements.
Advanced Detection Methods
Multi-sensors
Drones are equipped with multiple sensors that enable them to view the world around them. Stereo cameras give depth. Ultrasonic sensors detect objects on the ground. The use of IR sensors is typically during nighttime or in low-light conditions.
Sensor Fusion
Drones can simultaneously process all data from their sensors. This assists in developing a 3D map of their surrounding. The map enables the drone to avoid hitting the ground.
Automatic Rerouting of the Path
As it returns home, the drone continues to look ahead. Should it notice that in its path, it alters direction immediately. This allows it to soar through trees, poles, or walls at a time.
Safe Altitude and Distance Control
The system maintains a safe distance around the drone’s surroundings. It also selects the appropriate height in a way that avoids most ground hazards. This is aimed at choosing the safest possible route back to the home point.
Continuous Improvement
This includes repeated firmware and software upgrades of all drones. Such updates enable obstacle detection to become more accurate, allowing the drone to be safe in most possible conditions.
On each model, firmware and software enhancements are made. They continue to improve in identifying barriers and addressing various circumstances.
This contains changes in light, weather, or things in motion, such as birds. This is what makes DaaS a reliable business solution, thanks to its high degree of automation and security.
This safety system is used in the ZenaDrone 1000. It provides a secure, intelligent return-to-home drone capability.
Common Problems with Return-to-Home and How to Fix Them
RTH is improving progressively; however, it still has some flaws. Even the best RTH feature can experience problems that occur only occasionally. A good pilot should know how to quickly fix these problems. Being aware of these potential failures is crucial for ensuring safety at work.
| Problem | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| RTH Fails to Start | Insufficient GPS signal lock, outdated firmware, compass error, or low controller battery. | Wait for a solid GPS lock, update firmware on both drone and controller, calibrate the compass, and check controller battery level. |
| Drone Returns to Wrong Location | Home point recorded before full GPS lock or dynamic home point disabled. | Review flight logs for home point coordinates, confirm the home point in the app, and manually update it if you move. |
| GPS Not Locking | Interference from metal objects, insufficient satellites, or drone flying in ATTI mode. | Move away from metal structures, fly in open areas, and ensure the drone does not enter ATTI mode. |
| Firmware or Compass Issues | Outdated or malfunctioning software, or improper compass setup for the flight location. | Calibrate the compass before flying in new locations and regularly install official firmware updates. |
Most of the time, pilots can avoid these problems completely. They happen because the pilot didn’t prepare properly before the flight. Always complete a thorough pre-flight checklist. This ensures that RTH is as accurate as possible.
Tips for Using RTH Safely and Effectively
The optimal RTH feature relies on the use of the pilot. These guidelines are simple on how to use it safely and effectively. These are the tips that apply to all professional drones returning home.
- Wait for Full GPS Signal Lock: Don’t start until the app indicates a stable GPS fix. Always wait for the app to confirm the home point before proceeding.
- Adjust the right home point: When flying away from a moving object, ensure the dynamic home point is enabled. If you fly off a still point, verify that the point of launch is correct.
- Maintain the firmware: It is important to update the system when required to update the drone, controller, and battery firmware. Updates correct significant issues that improve RTH.
- Keep out of interference: Stay away from cell towers, big metal objects, and power lines. They can mess up the GPS and compass.
- Test RTH in the open space: At the start of a short flight, turn on RTH. This is to make sure it works and that the home point is correct.
- Establish a safe RTH altitude: Look for the largest obstacles in your flight path. To make sure the drone is clear, raise the RTH altitude above the barriers.
These tips turn RTH from a simple button into a strong safety plan.
Future of Return-to-Home in Drones
The future of RTH on drones is highly exciting and getting highly automated. It is more than simply adhering to predetermined GPS positions. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are rapidly transforming the way drones operate autonomously.
We believe that full AI-powered RTH systems will be the industry trend in the near future. Such systems will not take a fixed direction. They will instead transform during the flight based on incoming sensor data.
They will also attempt to detect the challenges at hand before they strike. They will choose the most optimal path to take to be fast and consume the minimum battery. Picture a drone that can figure out how to get back home. It also examines wind and battery wear at any time and then selects the safest and fastest route back.
This occurs as the second major leap of accurate RTH. Our models also follow this significant, continuous development. Our flight controllers are being equipped with sophisticated AI.
This makes our platforms remain avant-garde. All DaaS missions stay safe and successful due to the continuous introduction of new ideas.
Best Drones with Reliable RTH Features
Drones should be able to return to the point they started consistently, and that is one of the fundamental necessities for all DaaS professionals. Our drones are well-designed with reserve mechanisms and precise engineering. They act in accordance with the industry expectation.
This showcase highlights our commitment to high standards of self-navigation.
The focus here is on the credibility of the Return-to-Home functionality and its ideal professional uses.
| Drone Model | RTH Reliability Feature Excellence | Ideal Professional Use |
|---|---|---|
| ZenaDrone 1000 | AI-powered Return-to-Home system using multiple GPS receivers and vision sensors for highly accurate positioning and safe autonomous landing. | Large-scale operations such as agricultural surveys, factory inspections, and infrastructure mapping. |
| IQ Nano | Simple and intelligent failsafe RTH that activates during low battery or signal loss, reducing home point selection errors. | Suitable for beginners and professionals requiring quick setup and reliable basic operations. |
| IQ Square | Dual-GPS system with shared sensors dynamically adjusts flight paths, maintaining reliable RTH even in windy or harsh conditions. | Prosumer and advanced consumer use in outdoor and challenging environments. |
End Note
RTH on drones isn’t just a feature that comes with them. It shows that drone technology is the safest and most reliable.
It ensures that your drone comes back safely. As a professional pilot, you’ll have the power to make informed decisions if you know exactly how RTH works. You can trust the return home completely.
Highly successful RTH is the standard of professional performance. We are a trusted company in the application of advanced RTH technology. It is an operational risk in itself, from which we build our entire systems.
Experience our cutting-edge drone models firsthand with a test drive in the modern world. You can see how the ZenaDrone 1000 and IQ Series can help your business better.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does RTH mean on a drone?
RTH means Return-to-Home. It is a safety measure that returns the drone to its predetermined home point.
When does RTH activate automatically?
When the battery is extremely low or the controller signal is lost, RTH (also known as Failsafe RTH) will automatically activate.
Can RTH avoid obstacles?
Yes, advanced return-to-home systems combine visual, infrared, and ultrasonic sensors to view the drone’s position and locate the optimal path, ensuring the system is less prone to errors and crashes.
How does RTH work in ZenaDrone 1000?
The ZenaDrone 1000 has its own RTH system, which employs the GPS of other sensors and intelligent software. It ascends to a safe height and completes the safest, fastest route in the most efficient RTH performance.